
Check out our new Reading Series Series for Elementary age Students! |
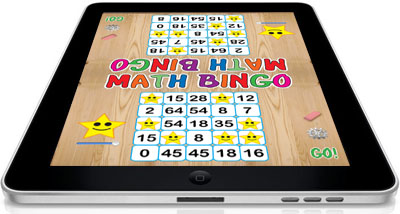
Math Bingo K-3 is a two player game that provides practice in addition, subtraction, multiplication, division and other math skills. Twenty different levels of problems can be selected. The levels are keyed to the Common Core Standards and are identified by standard numbers. Within each of the levels problems are randomly generated so every game is a unique experience. [ See also Math Bingo K-6 ] |
Select from 30 Different Game Levels Based on the Common Core Standards for Mathematics Tap the settings icon and use a slider to select an appropriate level for the game. Once the skill level has been selected the players tap the 'GO' button to indicate that they are ready to begin. Randomly generated math problems flash on the screen at the selected level. Each student tries to make a bingo by getting five markers in a row or column on a 5 x 5 game board. The first student to get five markers in a row or column wins the round. |
 |
This two-player game is challenging and fun. Students sit opposite each other with the iPad flat on a table between them. The game provides fast action as students develop a clever strategy to win a bingo. |
 |
Level |
Standard |
Description | Number Range |
CCS Code |
| 1 | Measurement and Geometry | Recognize Colors and Shapes. Color words: red, yellow, green, blue, purple, white, and black. Shape words: square, triangle, rectangle, circle, oval, star, diamond, plus and heart | N/A |
K.G.A.2 |
2
|
Counting & Cardinality |
Matching Sets and Numbers. Given a number written in words recognize the set with the same number of objects. |
Integers from 0 to 9 |
K.CC.B.4a |
3 |
Counting & Cardinality | Match Words to Numeric Symbols. Students are presented with the name of a number and must match it to the symbol. |
Integers from 0 to 20 | K.CC.B.4a |
4 |
Operations and Algebraic Thinking | Add within 20. Students are shown two sets of objects as an addition problem. The object is to select the correct answer. |
Integers from 1 to 20 | 1.OA.6 |
5 |
Operations and Algebraic Thinking | Determine the unknown whole number in an addition or subtraction equation relating three whole numbers. |
Integers from 1 to 10 | 1.OA.D.8 |
6 |
Operations and Algebraic Thinking | Determine the unknown whole number in an addition or subtraction equation relating three whole numbers. |
Integers from 1 to 20 | 1.OA.D.8 |
7 |
Operations and Algebraic Thinking | Determine the unknown whole number in an addition equation. | Integers from 1 to 20 | 1.OA.D.8 |
8 |
Operations and Algebraic Thinking | Determine the unknown whole number in a subtraction equation. | Integers from 1 to 10 | 1.OA.D.8 |
9 |
Operations and Algebraic Thinking | Determine the unknown whole number in a subtraction equation. | Integers from 1 to 20 | 1.OA.D.8 |
10 |
Operations and Algebraic Thinking | Represent and solve problems involving addition and subtraction - Solve problems that call for addition of three whole numbers whose sum is less than or equal to 20. |
Integers from 1 to 20 | 1.OA.A.2 |
11 |
Numbers and Operations in Base Ten | Extend the counting sequence. Count to 120, starting at any number less than 120. |
Integers from 0 to 120 | 1.NBT.A.1 |
12 |
Numbers and Operations in Base Ten | Use place value understanding and properties of operations to add and subtract. |
Integers from 0 to 100 | 1.NBT.C.4 |
13 |
Measurement and Data | Tell and write time in hours and half-hours using analog and digital clocks. |
Number Range: Hour and half-hour times. | 1.MD.B.3 |
14 |
Numbers and Operations in Base Ten | Given a two-digit number, mentally find 10 more or 10 less than the number, without having to count; explain the reasoning used. |
Number Range: Integers from 0 to 100 | 2.NBT.5 |
15 |
Numbers and Operations in Base Ten | Use place value understanding and properties of operations to add and subtract. Subtract multiples of 10 in the range 10-90 from multiples of 10 in the range 10-90 (positive or zero differences). | Integers from 10 to 90 | 2.NBT.6 |
16 |
Numbers and Operations in Base Ten | Mentally add 10 or 100 to a given number 100–900, and mentally subtract 10 or 100 from a given number 100–900. |
Integers from 10 to 100 and 100 to 900 | 2.NBT.8. |
17 |
Number and Operations in Base Ten | Understand place value. Count within 1000; skip-count by 5's, 10's and 100's. |
Integers from 0-1000 | 2.NBT.A.2 |
18 |
Number and Operations in Base Ten | Use place value understanding and properties of operations to add and subtract. Fluently add and subtract within 100 using strategies based on place value, properties of operations, and/or the relationship between addition and subtraction. | Factors from 0 to 100 | 2.NBT.B.5 |
19 |
Numbers and Operations in Base Ten | Use place value understanding and properties of operations to add and subtract. Mentally add 10 or 100 to a given number 100–900, and mentally subtract 10 or 100 from a given number 100–900. | Factors from 100 to 900 | 2.NBT.B.8 |
20 |
Numbers and Operations in Base Ten | Understand place value. Read and write numbers to 1000 using base ten numerals, number names, and expanded form. |
Factors from 100 to 900 | 2.NBT.A.3 |
| 21 | Numbers and Operations in Base Ten | Use place value understanding and properties of operations to add and subtract. Add up to four two-digit numbers using strategies based on place value and properties of operations. | Integers from 10 to 99 | 2.NBT.A.6 |
| 22 | Operations and Algebraic Thinking | Represent and solve problems involving multiplication and division. Determine the unknown whole number in a multiplication or division equation relating three whole numbers. | Factors from 0 to 100 | 3.OA.7 |
| 23 | Operations and Algebraic Thinking | Understand properties of multiplication and the relationship between multiplication and division. Apply properties of operations as strategies to multiply and divide. | Factors from 0 to 100 | 3.OA.5 |
| 24 | Operations and Algebraic Thinking | Fluently multiply within 100. | Factors from 0 to 10 | 3.OA.7 |
| 25 | Number & Operations in Base Ten | Use place value understanding and properties of operations to perform multi-digit arithmetic. Fluently add and subtract within 1000 using strategies and algorithms based on place value, properties of operations, and/or the relationship between addition and subtraction. | Integers from 0 to 10 | 3.NBT.A.2 |
| 26 | Number & Operations in Base Ten | Use place value understanding and properties of operations to perform multi-digit arithmetic. Multiply one-digit whole numbers by multiples of 10 in the range 10–90 (e.g., 9 × 80, 5 × 60) using strategies based on place value and properties of operations. | Integers from 10 to 90 | 3.NBT.A.3 |
| 27 | Number & Operations | Fractions - Understand a fraction 1/b as the quantity formed by 1 part when a whole is partitioned into b equal parts; understand a fraction a/b as the quantity formed by a parts of size 1/b. | Fractions from 1/2 - 9/10 | 3.NF.A.1 |
| 28 | Number & Operations | Fractions - Recognize and generate simple equivalent fractions, e.g., 1/2 = 2/4, 4/6 = 2/3. Explain why the fractions are equivalent, e.g., by using a visual fraction model. | Fractions from 1/2 - 9/10 | 3.NF.A.3b |
| 29 | Operations and Algebraic Thinking | Represent and solve problems involving multiplication and division. Use multiplication and division within 100 to solve word problems in situations involving equal groups, arrays, and measurement quantities, e.g., by using drawings and equations with a symbol for the unknown number to represent the problem. | Whole Numbers 0-100 | 3.OA.A.3 |
| 30 | Operations and Algebraic Thinking | Represent and solve problems involving multiplication and division. Determine the unknown whole number in a multiplication or division equation relating three whole numbers. For example, determine the unknown number that makes the equation true in each of the equations 8 × ? = 48, 5 = _ ÷ 3, 6 × 6 = ?. | Whole Numbers 0-100 | 3.OA.A.4. |
| Based on Common Core Standards © Copyright 2010. National Governors Association Center for Best Practices and Council of Chief State School Officers. All rights reserved. |
$1.99 |

